G7400 RGB Modification
This modification is meant for G7400 models that lack an RGB/SCART port (i.e.: consoles not manufactured in France). It requires an RGB monitor with analog (not digital/TTL) inputs. The monitor should also be able to display PAL, or at least, have vertical hold and vertical size adjustments.
If you have not already done so, you may want to download the G7400 PCB schematics first. This is a 1 Mb download.
Parts List:
- 1x resistor 47E
- 1x resistor 330E
- 3x resistor 560E
- 3x resistor 1k
- 3x resistor 1k5
- 1x resistor 2k7
- 1x transistor BC547B
- 1x TTL IC 7407
- 7x diode 1N4148
- 1x DIN connector 8 pin (Hirschmann part #MAB-8-SH)
Tools:
- Small screwdriver
- Large screwdriver
- Soldering iron (grounded! With a fine tip)
- Desoldering tool or fine drill (0.8 mm)
- Wire cutter
Cautions:
- Be sure to unplug the console from the power outlet, because the power supply inside the console is NOT isolated.
- Be careful not to damage the keyboard cable.
- There's a big chance you will need to resolder the 3 wires between the power supply and the main PCB after you're finished.
- The 8-pin DIN connector may be hard to find – you may have to make your own RGB cable.
- There are two versions of the 8-pin DIN connector – they look almost the same, but the place of some pins is a little different and the numbering also differs. The one used in the G7400 is manufactured by Hirschmann, part #MAB-8-SH. (Thanks to Dominic Bode for this information!)
- This mod is meant only for analog 75 Ohm RGB inputs.
What To Do:
- After switching off the console, wait a few minutes, otherwise the capacitors of the power supply might still contain dangerous voltages.
- Turn the console upside down, unplug the controllers, remove the 5 screws, remove the bottom plate, remove the 2 large screws which hold the larger PCB, unplug the RF modulator connector and gently flip the PCB.
- Remove the plastic black clip on the PCB next to the joystick connector. This is where the RGB connector is going to be placed.
- The area of the chip (7407) might be covered partly by a label which should be removed.
- Remove the solder from the holes which are needed for the extra components. This might be difficult because the PCB is double sided and the holes are plated-through. You can use a special desoldering tool, but you can also use a very fine drill (0.8 mm). When you use a desoldering iron, make sure that it's grounded! Check the part number list below to see which holes should be cleared. These part numbers are printed on the PCB.
- Now solder the new components according to the part numbers list, see also Figure 1 and Figure 2 (684 and 769 are not there yet). The resistor of 2k7 should be soldered at the back of the PCB according to the picture. Check the correct positioning of chip 7407 and the diodes!
- Put the PCB back in its place, then check if the solder joints of the three power supply wires are still OK. You don't need to plug the RF modulator back in.
- Before testing, put the bottom plate back to avoid a dangerous electric shock.
Part Numbers (these are printed on the PCB):
| 683 = 7407 | (RGB) |
| 684 = BC547B | (Video) |
| 685 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 686 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 687 = 1N4148 | (SCART only) |
| 701 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 702 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 703 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 704 = 1N4148 | (RGB) |
| 740 = 560E | (RGB) |
| 741 = 560E | (RGB) |
| 742 = 560E | (RGB) |
| 743 = 1k5 | (RGB) |
| 744 = 1k5 | (RGB) |
| 745 = 1k5 | (RGB) |
| 764 = 1k | (Sound) |
| 765 = 330E | (Sound) |
| 769 = 1k | (Video) |
| 772 = 1k | (SCART only) |
| 773 = 47E | (SCART only) |
| J4 = 8-pin DIN connector | |
at back of PCB:
| resistor 2k7 | (Video) |
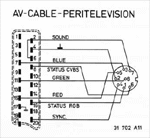
DIN Connector Pinout
1: RGB status (75 Ohm, 3 V)
2: Ground (0 V)
3: Blue (75 Ohm, 0.7 Vtt)
4: Composite Video (CVBS) (75 Ohm, 1 Vtt)
5: Red (75 Ohm, 0.7 Vtt)
6: Status CVBS (VCR) (10 kOhm, 12 V)
7: Sound
8: Green (75 Ohm, 0.7 Vtt)
Some voltages will be higher when the outputs are not terminated correctly.